Health
Texas A&M Researchers Develop Nanoflowers to Boost Stem Cell Energy
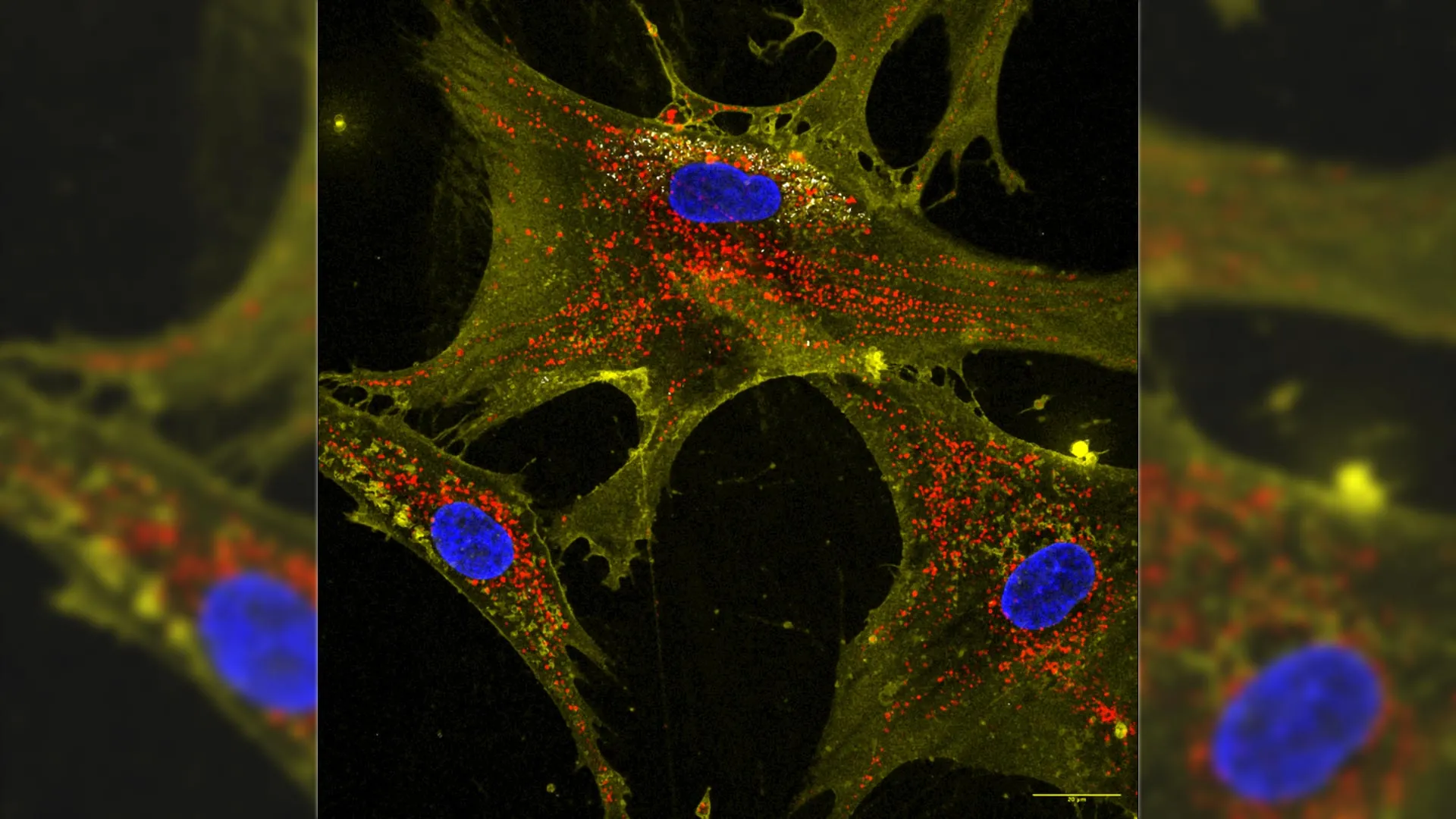
Biomedical researchers at Texas A&M University have made a significant breakthrough in enhancing stem cell functionality. They discovered that microscopic particles known as nanoflowers can double the production of mitochondria in stem cells. This advancement allows the energized stem cells to share their excess mitochondria with weakened cells, potentially revitalizing them and enhancing their energy production.
The research, published on November 27, 2025, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, highlights a novel approach to combat the decline in cellular energy associated with aging and degenerative diseases. Dr. Akhilesh K. Gaharwar, a professor of biomedical engineering, and Ph.D. student John Soukar led the study, illustrating how their technique could address various health conditions linked to mitochondrial decline.
Aging and damage from diseases such as Alzheimer’s significantly reduce the number of mitochondria within cells, leading to decreased energy levels and functionality. The research team aimed to tackle this problem by creating a method that allows healthy stem cells to act as mitochondria donors, thereby restoring vitality to adjacent damaged cells.
Nanoflowers Enhance Mitochondrial Production
The innovative technique involves exposing stem cells to the nanoflower particles, which are composed of molybdenum disulfide. These particles enable the stem cells to produce two to four times more mitochondria than untreated cells. Once these enhanced stem cells come into contact with damaged or aging cells, they transfer the surplus mitochondria, effectively rejuvenating the recipient cells.
According to Gaharwar, “We have trained healthy cells to share their spare batteries with weaker ones.” This dynamic process not only boosts energy levels but also enhances the resilience of previously damaged cells. Notably, these cells demonstrated improved resistance to harmful treatments, such as chemotherapy, following mitochondrial supplementation.
The research team emphasized that while cells naturally exchange small amounts of mitochondria, the nanoflower-treated stem cells can transfer significantly larger quantities. Soukar remarked, “It’s like giving an old electronic a new battery pack,” highlighting the efficient energy restoration achieved through this innovative approach.
Promising Future for Mitochondrial Therapies
Previous methods to increase mitochondrial numbers within cells often require repetitive treatments due to their temporary effects. In contrast, the larger nanoparticles used in this study remain within the cell longer, continuously stimulating mitochondrial production. This suggests that therapies utilizing this nanoflower technology may only need to be administered once a month, enhancing patient compliance and reducing treatment frequency.
Gaharwar expressed optimism about the implications of their findings, stating, “If we can safely boost this natural power-sharing system, it could one day help slow or even reverse some effects of cellular aging.” The versatility of this technique opens the door to potential applications across various tissues in the body, targeting conditions such as cardiomyopathy and muscular dystrophy.
The project received funding and support from multiple organizations, including the National Institutes of Health, the Welch Foundation, the Department of Defense, and the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas. Additional contributions came from Texas A&M’s President’s Excellence Fund and the Texas A&M Health Science Center Seedling Grant. Key collaborators in the research included Texas A&M researchers Dr. Irtisha Singh, Dr. Vishal Gohil, and Dr. Feng Zhao.
As research progresses, the team anticipates further exploration into the use of nanoflowers in stem cell treatments, paving the way for innovative therapies that could transform the landscape of regenerative medicine.
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoDiscover Reese Witherspoon’s Chic Dining Room Style for Under $25







