Science
Ribosome Collisions Trigger Emergency Stress Responses in Cells
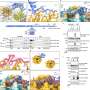
Ribosomes, the essential protein factories of all living organisms, have been found to trigger emergency stress responses when they collide with one another. A recent study conducted by researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, published in the journal Nature Communications, reveals that this collision can disrupt normal protein synthesis, prompting cells to initiate defensive mechanisms.
Ribosomes play a critical role in translating genetic information into functional proteins. They bind to messenger RNA (mRNA) and traverse along the strand, decoding the genetic instructions and linking amino acids to form proteins. This fundamental process is vital for cell growth and function.
The research highlights that when ribosomes collide, they can cause significant stress within the cell. The study found that cells activate stress responses to mitigate the damage, thereby ensuring that protein synthesis can continue effectively. This discovery sheds light on the intricate balance that cells must maintain to function optimally.
The significance of ribosome collisions extends beyond basic cellular biology. The findings may have implications for understanding various diseases, including cancer, where protein synthesis is often dysregulated. By better understanding how cells respond to ribosome collisions, researchers may develop new therapeutic strategies to address such conditions.
Researchers observed that under normal circumstances, ribosomes operate smoothly along the mRNA strand. However, when there is an overload of ribosomes or they encounter obstacles, collisions become more likely. This can lead to a decrease in protein production, which may trigger a series of stress responses aimed at restoring homeostasis within the cell.
In their experiments, the team utilized advanced imaging techniques to visualize ribosome behavior in real-time. They discovered that when collisions occur, it leads to an increase in the production of specific stress response proteins. These proteins help stabilize the cellular environment and allow the ribosomes to resume their function after the stress has been addressed.
The implications of these findings are profound. As cells encounter various stressors—ranging from environmental challenges to genetic mutations—understanding the mechanisms behind ribosome collisions can provide valuable insights into cellular resilience. The research not only enhances our knowledge of fundamental biology but also opens new avenues for medical research aimed at combating diseases linked to protein synthesis errors.
The study underscores the importance of ribosomes in maintaining cellular health and highlights the potential consequences of their malfunction. As scientists continue to explore the complexities of cellular responses, this research may pave the way for innovative approaches to treat diseases where ribosome function and protein synthesis are compromised.
Continued research in this area promises to deepen our understanding of cellular mechanics, ultimately contributing to advancements in therapeutic strategies and improved health outcomes.
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoDiscover Reese Witherspoon’s Chic Dining Room Style for Under $25








