Health
Harvard Study Uncovers Metabolites Linked to Obesity Control
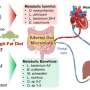
A recent study from Harvard University has revealed that specific metabolites produced in the intestine play a critical role in regulating obesity and type 2 diabetes. These metabolites travel from the intestine to the liver and subsequently to the heart, where they are distributed throughout the body. This groundbreaking research highlights the importance of these metabolites in controlling metabolic pathways in the liver and enhancing insulin sensitivity.
The findings, published in the journal Cell Metabolism, suggest that targeting these metabolites could pave the way for innovative treatments aimed at combating obesity and its associated health issues. The research team, led by experts in metabolic health, identified a distinct set of metabolites that significantly influence metabolic processes.
Implications for Treatment
Understanding the role of these metabolites opens new avenues for developing therapeutic strategies. The study indicates that enhancing metabolite activity could improve insulin sensitivity, a crucial factor in managing type 2 diabetes. As the prevalence of obesity and diabetes continues to rise globally, this research could offer valuable insights into preventive and treatment measures.
The implications of these findings extend beyond immediate health concerns; they highlight the intricate connections between diet, gut health, and metabolic regulation. By focusing on how metabolites influence insulin responses, researchers may be able to create targeted interventions that address the root causes of metabolic disorders.
Future Research Directions
Moving forward, the research team plans to delve deeper into the mechanisms by which these metabolites affect metabolic health. Further studies will aim to assess how dietary choices can modify metabolite production and, consequently, metabolic outcomes. This line of inquiry could revolutionize approaches to dietary recommendations and nutritional therapies for individuals at risk of obesity and diabetes.
The study underscores the importance of interdisciplinary research in tackling complex health issues. By integrating insights from biochemistry, nutrition, and endocrinology, researchers are better positioned to uncover effective strategies for improving public health.
As the global health community continues to grapple with the escalating rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes, findings from Harvard University serve as a timely reminder of the potential for scientific research to yield solutions that can enhance quality of life and reduce healthcare burdens. With ongoing investigations and a focus on metabolite-driven therapies, there is hope for a future where these conditions can be effectively managed or even prevented.
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoDiscover Reese Witherspoon’s Chic Dining Room Style for Under $25







