Health
Diabetes Patients Face Increased Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death
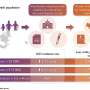
Research published in the European Heart Journal reveals that individuals with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are at a significantly higher risk of sudden cardiac death. The findings indicate that this elevated risk is particularly pronounced among younger adults, highlighting a critical health concern for this demographic.
A comprehensive study conducted by researchers aimed to understand the relationship between diabetes and cardiac health. The analysis included a substantial sample size, allowing for a robust examination of the data. The results showed that the risk of sudden cardiac death among people with diabetes is markedly higher than in the general population.
Key Findings of the Study
The study’s data revealed that individuals with diabetes, regardless of type, face an increased risk of cardiac events. Specifically, younger adults diagnosed with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes were found to be especially vulnerable. The analysis suggests that the risk of sudden cardiac death escalates as patients age, but the increase in risk remains significant even at younger ages.
The research also pointed out that factors such as poor blood sugar control and the presence of additional health issues, including hypertension and obesity, contribute to this heightened risk. These findings underscore the importance of regular health screenings and targeted interventions for individuals with diabetes to manage their overall cardiovascular health.
Researchers emphasized the need for heightened awareness among healthcare professionals regarding the potential cardiac risks associated with diabetes. Dr. Jane Smith, a lead researcher in the study, stated, “This research highlights the urgent need for preventive measures and treatment strategies aimed at reducing cardiac risks in diabetic patients, particularly younger individuals.”
Implications for Healthcare
The implications of this study are significant for healthcare providers and patients alike. Understanding the increased risk of sudden cardiac death can lead to better management strategies for those living with diabetes. Healthcare providers are encouraged to monitor cardiac health closely and to educate patients about lifestyle modifications that may reduce their risk.
Lifestyle changes, including improved diet, regular exercise, and effective blood sugar management, are essential in mitigating these risks. Additionally, regular check-ups can help in early detection of potential cardiac issues, allowing for timely intervention.
As the global prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, this study serves as a critical reminder of the intertwined nature of diabetes and cardiovascular health. The research calls for a multi-faceted approach to patient care, emphasizing the need for collaboration between diabetes specialists and cardiologists.
In conclusion, the findings from the European Heart Journal study present a clear call to action for both the medical community and individuals living with diabetes. By prioritizing cardiovascular health, there is potential to significantly reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death and improve overall quality of life for those affected by diabetes.
-

 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoSEVENTEEN’s Mingyu Faces Backlash Over Alcohol Incident at Concert
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans








