Politics
Researchers Enhance Understanding of Historical Building Materials
Preserving cultural heritage relies heavily on understanding the materials that comprise historical structures. A research team from the Department of Civil Engineering at Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University in Türkiye has published a comprehensive review titled “Materials Characterization of Historical Structures: A Review.” This study addresses significant gaps in the characterization of building materials essential for the conservation and restoration of historical sites.
The research highlights the importance of accurately determining the properties of materials used in historical buildings, including various natural stones and mortars. It emphasizes that the long-term survival of these structures depends on selecting appropriate restoration materials. Yet, challenges such as inadequate holistic analysis and unclear guidelines for characterization methods continue to hinder effective conservation efforts.
Comprehensive Evaluation of Characterization Techniques
The study systematically evaluates analytical methods for characterizing historical building materials. It synthesizes existing research and clarifies the strengths and limitations of various techniques, providing valuable guidance for future research methodology.
The authors, Mertcan Demirel, Alican Topsakal, and Muhammet Gökhan Altun (corresponding author), focus on four core categories of characterization techniques, which include:
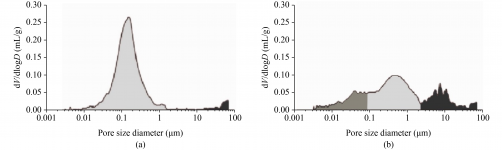
1. **Physical and Thermal Property Analysis**: Techniques such as Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP) are used to assess porosity and water permeability. For instance, studies on mortars from Amaiur Castle identified two primary pore size distributions, ranging from 0.01–1 μm and 1–10 μm. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) further evaluate thermal resistance, noting that calcite decomposes between 600–900 °C, resulting in a mass loss of 20%–40% due to CO2 emission.
2. **Chemical Property Analysis**: The study employs various techniques, including X-ray Diffraction (XRD) to analyze mineral composition, revealing that calcite and quartz are prevalent in numerous mortars. Additional methods such as X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), and Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) analysis have been instrumental in detecting elemental content and heavy metals, with notable findings of high lead and zinc concentrations in the black crusts of Seville Cathedral.
3. **Mechanical Property Analysis**: Non-destructive techniques like Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) correlate wave speed with concrete quality, while the Schmidt hammer measures surface hardness to estimate compressive strength. These approaches help evaluate mechanical performance without damaging historical structures.
4. **Visualization Techniques**: Advanced methods such as Scanning Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) and Infrared Thermography (IRT) allow for in-depth analysis of microstructural elements and hidden defects. For example, IRT has been effective in identifying invisible cracks in Malatya Taşhoran Church.
Significance of Multi-Method Approaches
The review underscores the necessity of employing multiple characterization methods to achieve consistent and reliable results. Extensive evaluations of benchmarks, including structures from the Roman period in Portugal, 11th–14th century buildings in Spain, and Mamluk-period structures in Egypt, validate the effectiveness of these techniques.
The findings from this research provide a data-driven foundation for scientific inquiry, potentially leading to cost reductions in the engineering and architectural analysis of historical structures. Furthermore, the insights gained from these comprehensive evaluations support the development of restoration projects based on scientifically grounded principles.
The full text of “Materials Characterization of Historical Structures: A Review” can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-025-1222-3. This study not only advances the field of cultural heritage preservation but also ensures that future generations can appreciate and learn from these vital historical connections.
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoLia Thomas Honored with ‘Voice of Inspiration’ Award at Dodgers Event
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoDiscover Reese Witherspoon’s Chic Dining Room Style for Under $25
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoFast & Furious Coaster Hits the Track at Universal Studios
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoResearchers Uncover New Insights into Cancer Mortality Causes









