Science
New Software Toolbox Transforms Brain Models with Data Learning

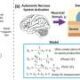
Researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking software toolbox designed to enable brain-like models to learn directly from data. Named JAXLEY, this innovative open-source framework merges the accuracy of biophysical models with the rapid adaptability of contemporary machine learning techniques. The findings, recently posted on the bioRxiv preprint server, represent a significant advancement toward developing faster and more precise simulations of brain function.
The development of JAXLEY could revolutionize the field of neuroscience by streamlining the process of simulating complex neural activities. Traditional methods often rely on detailed biophysical models, which, while accurate, can be time-consuming and computationally intensive. In contrast, JAXLEY utilizes modern machine learning approaches, allowing for quicker training and better scalability.
Researchers emphasize that this toolbox is not only powerful but also user-friendly, making it accessible for a wide range of scientists and engineers. By providing an open-source platform, the creators of JAXLEY aim to foster collaboration and innovation within the scientific community. As neuroscience continues to advance, tools like JAXLEY could play a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of the brain.
The implications of this research extend beyond neuroscience. With its ability to process vast amounts of data efficiently, JAXLEY may find applications in various fields that require complex data analysis and modeling. This includes areas such as artificial intelligence, cognitive science, and even robotics, where understanding brain-like processes can lead to more sophisticated algorithms and systems.
In the study published on bioRxiv, researchers demonstrated JAXLEY’s capabilities through several simulations that showcased its effectiveness in training models to mimic brain-like functions. The results indicated that JAXLEY can significantly outperform traditional approaches in both speed and accuracy, marking a pivotal moment in computational neuroscience.
As the scientific community begins to adopt this new toolbox, researchers are optimistic about the potential breakthroughs in understanding neural networks and their impact on behavior, cognition, and even mental health. The integration of machine learning with biophysical modeling could pave the way for new therapies and interventions for various neurological conditions.
In summary, the introduction of JAXLEY represents a substantial leap forward in the simulation of brain function. By combining the strengths of machine learning and biophysical models, this open-source framework not only enhances research capabilities but also sets the stage for future innovations in neuroscience and beyond. As researchers continue to explore the possibilities offered by JAXLEY, the future of brain modeling looks increasingly promising.
-

 Top Stories4 weeks ago
Top Stories4 weeks agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Top Stories4 weeks ago
Top Stories4 weeks agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Lifestyle4 weeks ago
Lifestyle4 weeks agoDiscover Reese Witherspoon’s Chic Dining Room Style for Under $25
-

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Lifestyle4 weeks ago
Lifestyle4 weeks agoLia Thomas Honored with ‘Voice of Inspiration’ Award at Dodgers Event