Science
New Study Reveals Early Universe’s Black Holes and Stars Formation
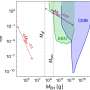
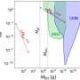
Research published in the journal Physical Review D suggests that within less than one second after the Big Bang, interactions among particles could have led to the formation of the universe’s earliest astronomical structures, including black holes, boson stars, and so-called cannibal stars. This groundbreaking study was conducted by a collaborative team from SISSA—Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati, alongside INFN, IFPU, and the University of Warsaw.
The study proposes that shortly after the universe began, particles may have condensed into halos of matter. These halos, as the research indicates, could then have undergone gravitational collapse, leading to the creation of some of the first black holes. This early phase of cosmic evolution is critical for understanding how large structures in the universe formed.
According to the researchers, the possibility of these primordial structures challenges existing theories about the formation of celestial objects. The concept of cannibal stars refers to massive stars that grow by merging with smaller stars. This study provides a theoretical framework suggesting that such stars might have emerged soon after the universe’s birth.
The implications of this research extend beyond mere theoretical interest. Understanding the formation of these ancient cosmic entities could illuminate processes that shaped the universe as we know it today. Given that this research stems from collaborations among several prestigious institutions, its findings contribute significantly to the fields of astrophysics and cosmology.
As research continues to evolve, the implications of these findings may lead to new insights into the early universe. The exploration of these primordial structures is not only an academic pursuit but may also enhance our understanding of the universe’s overall evolution. The collaborative effort highlights the importance of interdisciplinary research, bridging gaps between theoretical physics and observational astronomy.
Future studies will likely aim to gather observational evidence to support these theories, potentially using advanced telescopes and other technologies. As scientists continue to piece together the history of the universe, discoveries such as these provide a fascinating glimpse into the mysteries of cosmic evolution.
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 Top Stories4 weeks ago
Top Stories4 weeks agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Top Stories4 weeks ago
Top Stories4 weeks agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Lifestyle4 weeks ago
Lifestyle4 weeks agoDiscover Reese Witherspoon’s Chic Dining Room Style for Under $25
-

 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Health4 weeks ago
Health4 weeks agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoRemembering David E. Brest: A Life Dedicated to Nature and Family