Science
Researchers Discover Key Protein Influences Brain’s Reward Learning
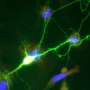
Groundbreaking research from Georgetown University Medical Center has revealed that a specific protein in the brain plays a crucial role in how individuals associate cues with rewards. The study indicates that alterations in the activity of this protein can significantly influence the learning process involved in recognizing beneficial outcomes versus detrimental habits, such as addiction to smoking.
Understanding the mechanisms behind reward learning is vital, as it directly impacts behavior. The research highlights that heightened or diminished activity of this key protein can dictate when individuals should respond positively to cues that lead to rewarding experiences. Conversely, it also affects their ability to ignore signals linked to harmful behaviors.
Implications for Addiction and Behavioral Change
The findings shed light on the underlying biological processes that govern learned behaviors, particularly in relation to addiction. For example, individuals struggling with smoking may find it challenging to resist cues that trigger cravings. By understanding how the protein alters these responses, researchers aim to develop targeted strategies for intervention.
The study underscores the complexity of the brain’s reward system. It reveals that the ability to differentiate between positive and negative cues is not merely a matter of willpower but is intricately linked to biological factors. This insight could pave the way for innovative treatments for various addictions and behavioral disorders.
Research in this domain is essential for creating effective therapeutic approaches. By manipulating the activity of this protein, scientists may be able to enhance the brain’s capacity to learn from positive experiences while diminishing the influence of negative cues. This dual approach could lead to more successful outcomes in treating addictive behaviors.
As the field of neuroscience continues to evolve, studies like this one from Georgetown University Medical Center contribute significantly to our understanding of the brain’s intricate functions. The implications extend beyond addiction, potentially influencing how individuals learn and adapt to various life situations.
In conclusion, the discovery of this key protein’s role in reward learning marks a significant advancement in neuroscience. As researchers delve deeper into these mechanisms, the potential for developing new therapeutic strategies becomes increasingly viable, offering hope for those looking to change ingrained behaviors effectively.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoSEVENTEEN’s Mingyu Faces Backlash Over Alcohol Incident at Concert
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans