Science
Roman Urbanism Linked to Decline in Health of Ancient Populations
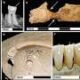
A recent study has confirmed that the health of populations in Roman Britain suffered significantly during the Roman occupation, particularly in urban areas. This research, conducted by a team from the University of Cambridge, analyzed skeletal remains from England dating back to the era before and during the Roman presence. The findings indicate that while urban centers experienced a marked decline in health, rural regions maintained their pre-Roman traditions, which likely contributed to better health outcomes.
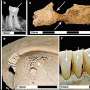
The analysis focused on skeletal remains from various sites, revealing notable differences in health indicators between urban and rural populations. Researchers identified evidence of malnutrition, dental diseases, and other health issues that were more prevalent in the cities of Roman Britain. In contrast, those living in rural areas appeared to retain healthier lifestyles and diets that were less impacted by the urbanization trends of the time.
Health Implications of Urban Living in Ancient Rome
The study highlights the long-term consequences of urban living during the Roman occupation. Skeletal remains from urban sites such as Londinium (modern-day London) showed significant signs of stress and nutritional deficiencies. These findings align with previous theories suggesting that the rapid growth of cities during this period created unhealthy living conditions, including overcrowding and poor sanitation.
Conversely, the rural populations, who continued to engage in traditional agricultural practices, did not exhibit the same health decline. This contrast suggests that the lifestyle and diet of rural inhabitants were more sustainable compared to their urban counterparts. The preservation of pre-Roman traditions likely played a crucial role in maintaining their health.
The research underscores the importance of understanding how urbanization impacts public health, a topic that remains relevant today. As cities continue to expand globally, lessons from the past can inform modern health policies and urban planning strategies.
Broader Context and Future Research
This investigation into the health effects of Roman urbanism is part of a larger effort to understand the relationship between environment, lifestyle, and health throughout history. The findings not only contribute to the field of archaeology and history but also raise questions about the implications of current urban living conditions.
The ongoing research aims to explore further the factors that led to health disparities between urban and rural populations during the Roman era. Future studies may delve into aspects such as diet, social structure, and the role of public health measures in ancient societies.
In conclusion, the study by the University of Cambridge provides valuable insights into how Roman urbanism affected health in ancient Britain, emphasizing the need to consider historical contexts when addressing contemporary health challenges. As urbanization continues to shape modern societies, understanding its historical impacts can guide efforts to improve health outcomes in urban settings today.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoSEVENTEEN’s Mingyu Faces Backlash Over Alcohol Incident at Concert
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts