Top Stories
Urgent Review Reveals Key Insights on Historical Material Analysis
UPDATE: A groundbreaking review from a team at Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University in Türkiye has just confirmed critical insights into the materials used in historical structures, with urgent implications for cultural heritage preservation. The study, titled “Materials Characterization of Historical Structures: A Review“, addresses significant gaps in our understanding of building materials essential for restoring and conserving ancient sites.
The research team, led by Mertcan Demirel, Alican Topsakal, and Muhammet Gökhan Altun, emphasizes that the survival of these structures relies heavily on understanding their construction materials—primarily natural stones and various types of mortars. The review highlights the need for comprehensive analysis methods to ensure effective restoration practices.
In a time when many historical landmarks are at risk, the review identifies persistent challenges in material characterization. These challenges include limited holistic analysis and a lack of clear guidance on methodologies, which impede scientific restoration efforts. The team systematically evaluated several core categories of characterization techniques, providing a crucial roadmap for researchers.
The review focuses on vital analytical methods, including:
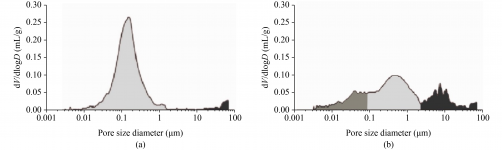
1. **Physical and Thermal Property Analysis**: Techniques such as Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP) reveal porosity and pore structure crucial for assessing water permeability. For instance, in mortars from Amaiur Castle, researchers identified two main pore size distributions between 0.01-1 μm and 1-10 μm.
2. **Chemical Property Analysis**: The team employed X-ray Diffraction (XRD) to determine mineral composition, notably finding calcite and quartz as predominant minerals in mortars. Other methods, such as X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) and Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) analysis, provided insights into elemental content, revealing alarming concentrations of heavy metals like lead and zinc in structures such as the Seville Cathedral.
3. **Mechanical Property Analysis**: Non-destructive methods, including Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) and Schmidt hammer tests, allow researchers to evaluate structural integrity without causing damage. This is critical when assessing the mechanical performance of fragile historical buildings.
4. **Visualization Techniques**: Advanced methods like Scanning Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) and Infrared Thermography (IRT) are highlighted for their ability to detect moisture and hidden defects, as demonstrated in the Malatya Taşhoran Church.
This comprehensive study not only synthesizes existing research but also clarifies the strengths and limitations of each technique, providing a data-driven foundation for future restoration projects. By employing multiple methods, researchers can achieve more consistent and reliable results, ultimately supporting the preservation of our cultural heritage.
The implications of this research are profound, extending beyond academic discourse to impact the preservation of historical sites worldwide. The review serves as a vital resource for engineers, architects, and conservationists, guiding them in the selection of appropriate methodologies for material analysis.
As the global community continues to grapple with the challenges of preserving historical structures, this urgent review underlines the importance of scientific approaches in restoration efforts. The paper titled “Materials Characterization of Historical Structures: A Review” is available for full access at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-025-1222-3.
Stay tuned for further developments as this story unfolds, highlighting the ongoing efforts to safeguard our shared cultural heritage for future generations.
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoLia Thomas Honored with ‘Voice of Inspiration’ Award at Dodgers Event
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoDiscover Reese Witherspoon’s Chic Dining Room Style for Under $25
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoFast & Furious Coaster Hits the Track at Universal Studios
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoResearchers Uncover New Insights into Cancer Mortality Causes









