Health
Study Links Muscle Strength and Visceral Fat to Brain Youthfulness

Recent research highlights the connection between muscle strength, visceral fat levels, and brain health. A study involving 1,164 adults utilized full-body MRI scans and artificial intelligence to explore how physical composition affects the biological age of the brain. The findings suggest that increased muscle mass and reduced deep abdominal fat correlate with a younger-looking brain, providing insight into how physical health can influence cognitive vitality.
This research will be presented at the upcoming annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America in early December 2023. The study indicates that individuals with higher muscle mass tended to have brains that appeared biologically younger, while those with greater ratios of visceral fat to muscle displayed signs of accelerated brain aging. Notably, subcutaneous fat, which is fat stored just beneath the skin, did not show a significant relationship with brain aging.
According to the senior study author, Cyrus Raji, M.D., Ph.D., maintaining a healthy balance of muscle and visceral fat could lower the risk of developing conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease. “Healthier bodies with more muscle mass and less hidden belly fat are more likely to have healthier, youthful brains,” Raji stated.
Practical Steps to Enhance Muscle and Reduce Visceral Fat
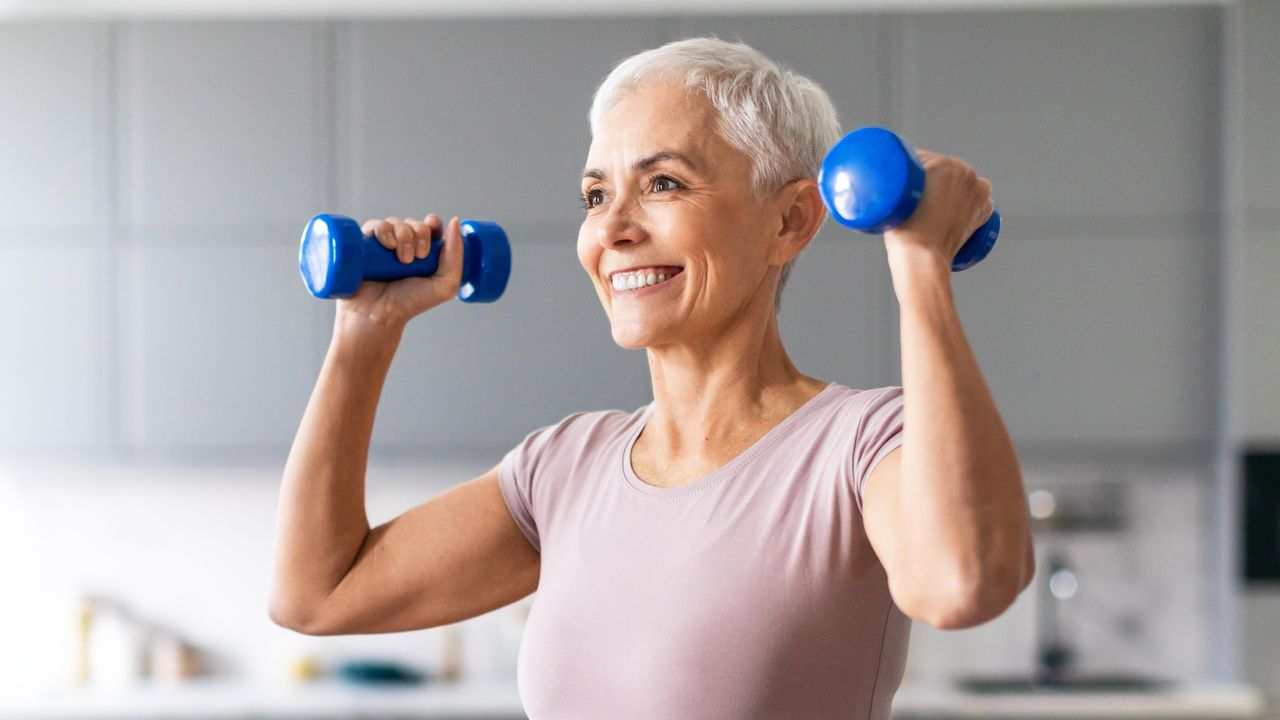
To translate these findings into actionable advice, we consulted with Josh Schlottman, a certified personal trainer. He outlined three effective strategies for building muscle and decreasing visceral fat.
Firstly, Schlottman recommends **interval sprinting** as a key method. “Interval sprinting is a form of high-intensity interval training that is the most effective form of exercise for getting rid of deep visceral fat. With HIIT, you also build more muscle mass in less time than traditional exercise,” he explained. For those new to running, the Jeffing technique, which combines short sprints with walking or easy jogging, is a more manageable approach to building speed and endurance.
Secondly, integrating **strength training with short HIIT circuits** can be particularly beneficial. Schlottman suggests using compound exercises like squats, lunges, push-ups, and pull-ups in a circuit format. “High-intensity resistance training like this builds muscle while at the same time burning calories and fat faster than weight lifting alone,” he noted.
Lastly, Schlottman emphasizes the importance of **smart nutrition basics**. He advises prioritizing protein intake, which is essential for muscle development and helps maintain satiety. Including fiber-rich foods such as spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, and beets can enhance feelings of fullness without encouraging overeating.
As more research underscores the link between physical health and cognitive function, individuals are encouraged to adopt practices that promote muscle growth and minimize visceral fat. Simple lifestyle changes can contribute significantly to both physical fitness and mental agility, reinforcing the idea that a strong body supports a healthy mind.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoDoctoral Candidate Trivanni Yadav Advances Battery Research at UTulsa
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoNASCAR Faces Fan Backlash as Steve Phelps’ Texts Surface
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoSEVENTEEN’s Mingyu Faces Backlash Over Alcohol Incident at Concert
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoRemembering David E. Brest: A Life Dedicated to Nature and Family