Science
Researchers Uncover Mechanism for Cell Quality Control in Calcium Channels
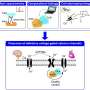
Researchers at Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany have made significant strides in understanding how cells manage quality control, specifically regarding calcium channels. An interdisciplinary team led by Prof. Patricia Hidalgo, along with Dr. Beatrix Santiago-Schübel and Dr. Mercedes Alfonso-Prieto, has uncovered the mechanisms by which cells identify and eliminate defective calcium channels. This groundbreaking work could have far-reaching implications for both basic science and the development of therapies for neurodegenerative diseases.
Understanding the Mechanisms of Cellular Quality Control
The collaboration among these three scientists highlights the importance of interdisciplinary research in tackling complex biological questions. Their findings reveal critical insights into the cellular processes responsible for maintaining calcium channel integrity. Calcium channels play a vital role in various cellular functions, including muscle contraction and neurotransmitter release. When these channels become defective, they can lead to severe cellular dysfunction and contribute to the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
The research, which was published in September 2023, illustrates how cells possess sophisticated mechanisms to monitor their internal components. The team discovered specific proteins that facilitate the recognition and removal of faulty calcium channels, thus ensuring the overall health of the cell. This process not only underscores the complexity of cellular operations but also emphasizes the potential for targeted therapeutic strategies in treating conditions linked to calcium channel abnormalities.
Implications for Future Therapies
The implications of this research extend beyond basic science. Understanding how cells manage defective components opens avenues for developing innovative treatments for neurodegenerative diseases. Conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease are characterized by the malfunction of calcium channels, leading to neuronal death and cognitive decline. By targeting the mechanisms revealed in this study, researchers might develop new strategies to restore cellular function and combat these debilitating diseases.
Furthermore, the interdisciplinary nature of this project showcases the value of collaborative research. By combining expertise from different fields, the team was able to approach the problem from various angles, ultimately leading to a more comprehensive understanding of cellular quality control. This model can serve as an example for future research initiatives aimed at addressing complex biological and medical challenges.
The ongoing work at Forschungszentrum Jülich represents a significant step forward in cellular biology and its application to medicine. As the scientific community continues to explore these mechanisms, the hope is that such discoveries will pave the way for effective therapies that could enhance the quality of life for millions affected by neurodegenerative diseases.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoDoctoral Candidate Trivanni Yadav Advances Battery Research at UTulsa
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoNASCAR Faces Fan Backlash as Steve Phelps’ Texts Surface
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoSEVENTEEN’s Mingyu Faces Backlash Over Alcohol Incident at Concert
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoRemembering David E. Brest: A Life Dedicated to Nature and Family