Science
Researchers Uncover New Pathways in Hydrogen Isotope Exchange
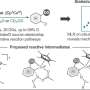
A recent study conducted by a collaboration between Professor Mónica H. Pérez-Temprano from the Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ) and Professor Anat Milo from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev has shed light on how the characteristics of specific substrates influence the reaction conditions in C–H deuteration reactions. This research is significant as it reveals how these factors dictate the pathways of hydrogen isotope exchange.
The findings were published in a leading scientific journal, providing valuable insights into the chemical processes involved. The team discovered that the nature of the substrates plays a crucial role in determining the necessary reaction conditions, ultimately guiding the course of the chemical reactions. This breakthrough could have far-reaching implications for various applications, including pharmaceuticals and materials science.
C–H deuteration reactions are vital in the field of chemistry, particularly for modifying compounds in a precise manner. The research indicates that the specific structural features of substrates can lead to distinct reaction pathways, which may alter the efficiency and outcomes of deuteration.
Implications for Future Research and Applications
The implications of this research extend beyond theoretical understanding. By identifying the precise conditions required for successful C–H deuteration, scientists can streamline processes in chemical synthesis. This could enhance the development of new drugs and materials that rely on isotopic labeling, which is essential for both analytical and therapeutic applications.
In the realm of drug development, for instance, the ability to manipulate hydrogen isotopes accurately can lead to the creation of more effective and targeted therapies. Similarly, in materials science, tailoring substrates to optimize reaction pathways can result in the innovation of new materials with specific properties.
Both Professor Pérez-Temprano and Professor Milo emphasized the collaborative nature of this research. The partnership between ICIQ and Ben-Gurion University exemplifies the importance of interdisciplinary cooperation in advancing scientific knowledge. As they continue to explore the intricacies of chemical reactions, the potential for new discoveries remains vast.
The study not only enriches the existing body of knowledge but also sets the stage for future investigations into hydrogen isotope chemistry. Researchers are now better equipped to design experiments that could lead to further breakthroughs in the field.
As the scientific community absorbs these findings, the hope is that this research will inspire new directions in chemical synthesis and foster innovations that can benefit various industries globally. The ongoing collaboration between these esteemed institutions highlights the importance of shared knowledge and research efforts in tackling complex scientific challenges.
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoSEVENTEEN’s Mingyu Faces Backlash Over Alcohol Incident at Concert
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans









