Science
New Deep Learning Tool Distinguishes Wild and Farmed Salmon

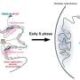
A recent study published in Biology Methods and Protocols reveals a groundbreaking advancement in identifying whether salmon is wild or farmed. Researchers have developed a deep learning tool that analyzes fish scales, providing a reliable method for distinguishing between the two types. This innovation could significantly enhance environmental protection strategies related to salmon populations.
The paper, titled “Identifying escaped farmed salmon from fish scales using deep learning,” details the methodology behind this tool. Researchers at the University of California, Davis, applied advanced machine learning techniques to analyze scale patterns. This approach offers a promising solution to a pressing ecological challenge, particularly concerning the impact of escaped farmed salmon on wild populations.
Potential Environmental Impact
The ability to accurately determine the origin of salmon is crucial for effective conservation efforts. Escaped farmed salmon can pose significant risks to wild salmon populations by competing for resources and interbreeding, potentially leading to genetic dilution. The new tool enables authorities to monitor and manage these populations more effectively, ensuring healthier ecosystems.
According to the study, deep learning algorithms were trained on a dataset of scale images from both wild and farmed salmon. The researchers achieved an impressive accuracy rate exceeding 95%, indicating the reliability of this method. With such high precision, this tool could prove invaluable for fisheries and environmental organizations.
Broader Applications and Future Prospects
The implications of this research extend beyond salmon. The techniques developed could potentially be adapted for other fish species, enhancing biodiversity conservation efforts across various aquatic environments. The use of deep learning in wildlife management is an emerging frontier, promising to revolutionize how scientists approach species identification and tracking.
As global attention turns to sustainability and environmental protection, innovations like this deep learning tool play a vital role. By improving the understanding of species populations, researchers can better inform policy decisions aimed at preserving ecological balance.
With the publication of this research in March 2024, the scientific community is poised to explore further applications of deep learning in ecology. As technology continues to evolve, so too does the potential for more sophisticated tools that can aid in the protection of our planet’s natural resources.
-

 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Red Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNew ‘Star Trek: Voyager’ Game Demo Released, Players Test Limits
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGlobal Air Forces Ranked by Annual Defense Budgets in 2025
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoMass Production of F-35 Fighter Jet Drives Down Costs
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoElectrification Challenges Demand Advanced Multiphysics Modeling
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoGold Investment Surge: Top Mutual Funds and ETF Alternatives
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoDirecTV to Launch AI-Driven Ads with User Likenesses in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoFreeport Art Gallery Transforms Waste into Creative Masterpieces
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoSEVENTEEN’s Mingyu Faces Backlash Over Alcohol Incident at Concert
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoUS Government Denies Coal Lease Bid, Impacting Industry Revival Efforts
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoGavin Newsom Critiques Trump’s Health and National Guard Plans